OKMOK
ALASKA, USA
53.43000° N, 168.13000° W
OVERVIEW
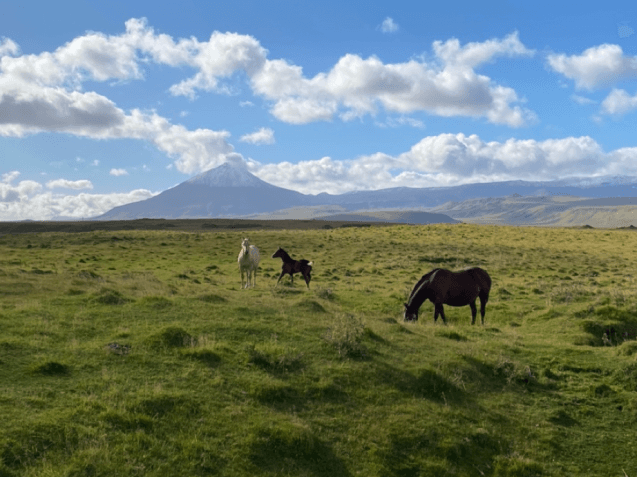
Okmok volcano is a large, caldera-forming volcano in the Aleutians
The basaltic Okmok shield volcano forms the NE end of Umnak Island in the Aleutian Islands. The summit of the low, 35-km-wide volcano is cut by two overlapping 10-km-wide calderas formed during eruptions about 12,000 and 2,050 years ago when dacitic pyroclastic flows reached the coast. More than 60 tephra layers from Okmok have been found overlying the 12,000-year-old caldera-forming tephra layer. Numerous cones and lava domes are present on the flanks down to the coast, including the SE-flank Mount Tulik, which is almost 200 m higher than the caldera rim. Some of the post-caldera cones show evidence of wave-cut lake terraces; more recent cones were formed after the caldera lake, once 150 m deep, disappeared. Eruptions have been reported since 1805 from cinder cones within the caldera, where there are also hot springs and fumaroles. Description from the Global Volcanism Program.
NETWORK HISTORY
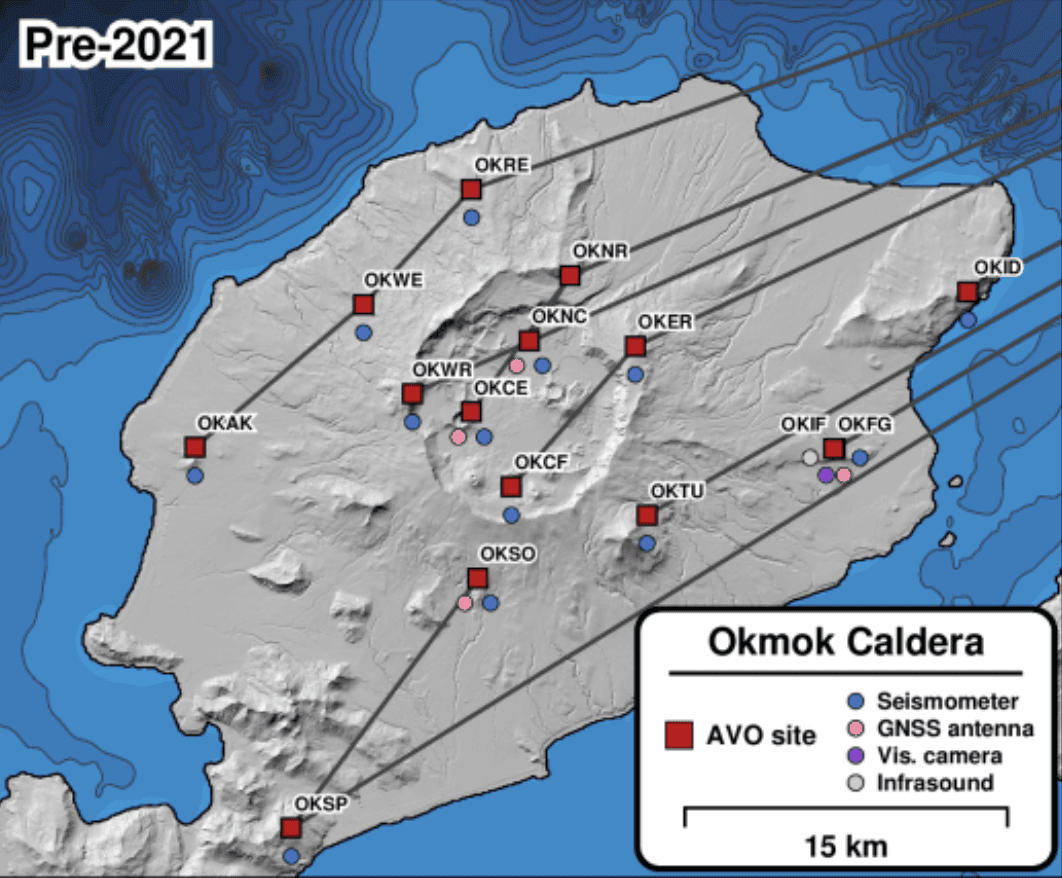
Okmok's network before and after AVERT
Compare how monitoring sites, instruments, and telemetry links have changed across different phases of deployment

RECOMMENDED FOR YOU
Related reading
SITES AND INSTRUMENTS
Okmok AK


